Startseite » Venturi pulse
VenturiPulse
Efficient aeration of standing water
with common submersible pumps
The VenturiPulse was developed in collaboration with the local chapters of THW Pfaffenhofen and Ratingen. Created by professionals, for professionals!

Picture example of successful ventilation
Compatibility
Compatible with various submersible pumps
Simple assembly
The swivel coupling enables easy installation
Fast deployment
Quick and easy to use near the shore

Quality standards
Robust quality made in Germany
Water aeration - how it works!
If the oxygen concentration in water bodies becomes too low due to high heat, biomass or pollution, they threaten to tip over. In such cases, the water must be aerated to prevent more serious damage. The targeted introduction of oxygen thus ensures the basis of life for fish and other aquatic organisms.
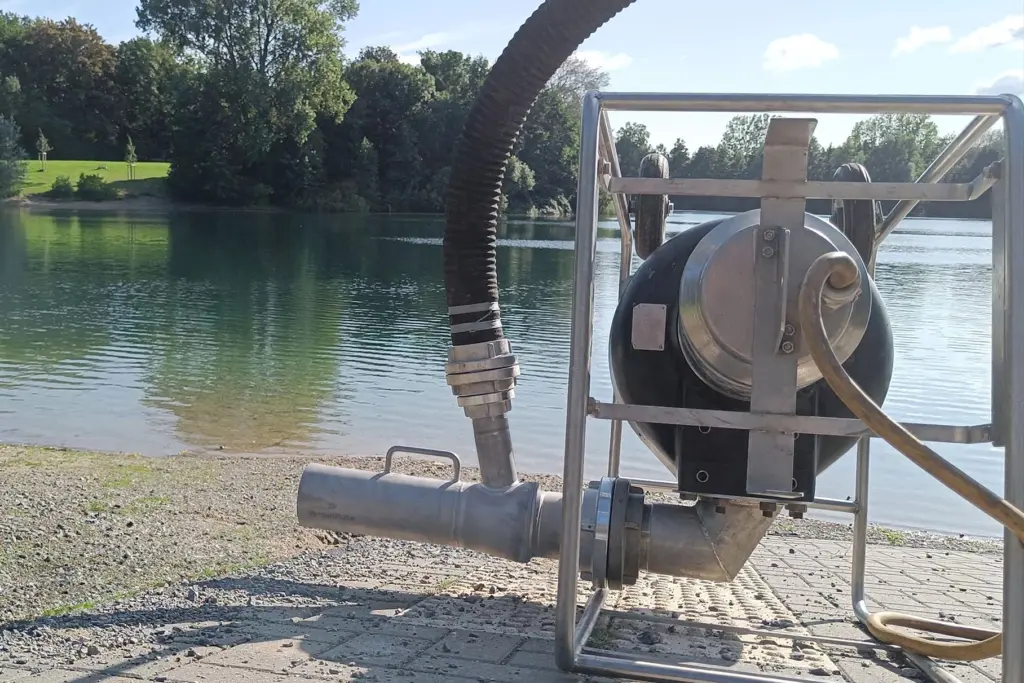

Simply attached to the discharge side of a submersible pump, air is supplied to the pumped liquid via the Venturi effect.
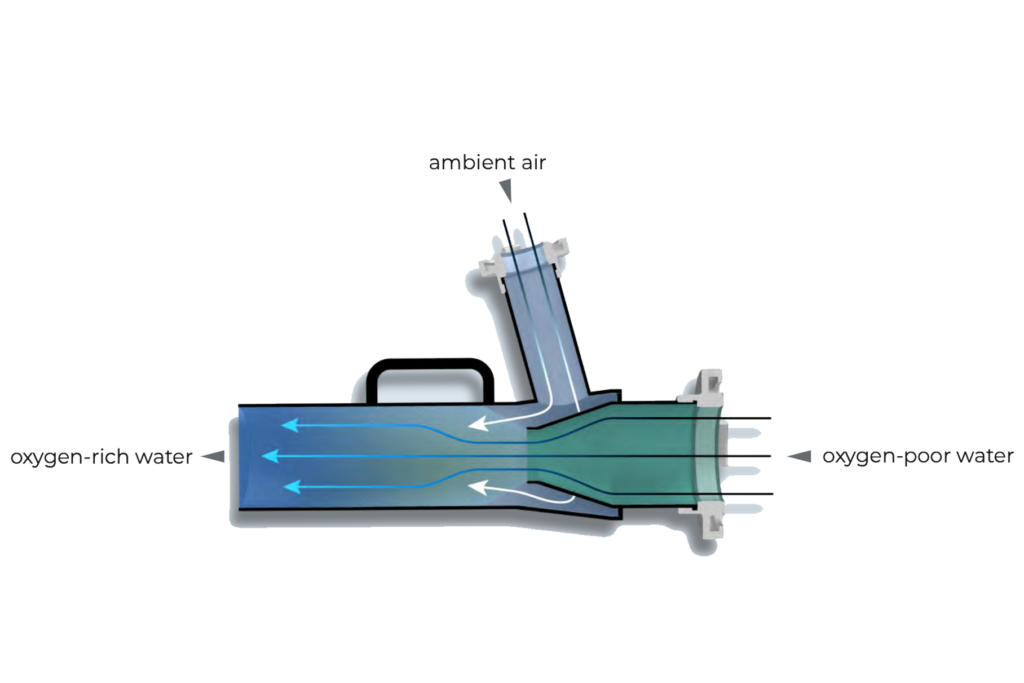
The suction effect is created solely by the flow of the pumped medium, i.e. no additional energy source is required.
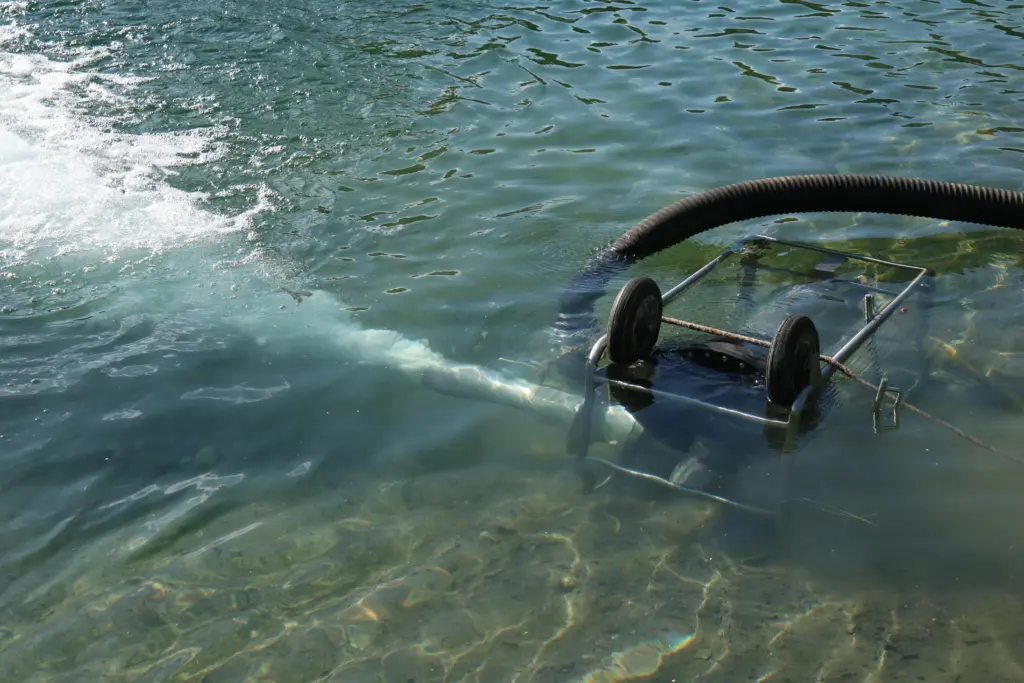

A fine bubble pattern is created, which favors the enrichment of oxygen in the water.
Product presentation (German)
Buy VenturiPulse online
You can purchase the VenturiPulse water aerator directly in our online shop.
Air enrichment through the Venturi effect
For healthy waters & biodiversity
The VenturiPulse water aerator can be used to create survival zones in bodies of water by enriching them with air.
- We recommend using at least two water aerators
- The ideal operating depth is between 0.5 and 2 meters
- Over a longer period of use, the entire body of water is enriched with sufficient oxygen
- The water aerator is suitable for near-surface water aeration
- Schnell im Einsatz eignet er sich als Teichbelüfter und Seebelüfter
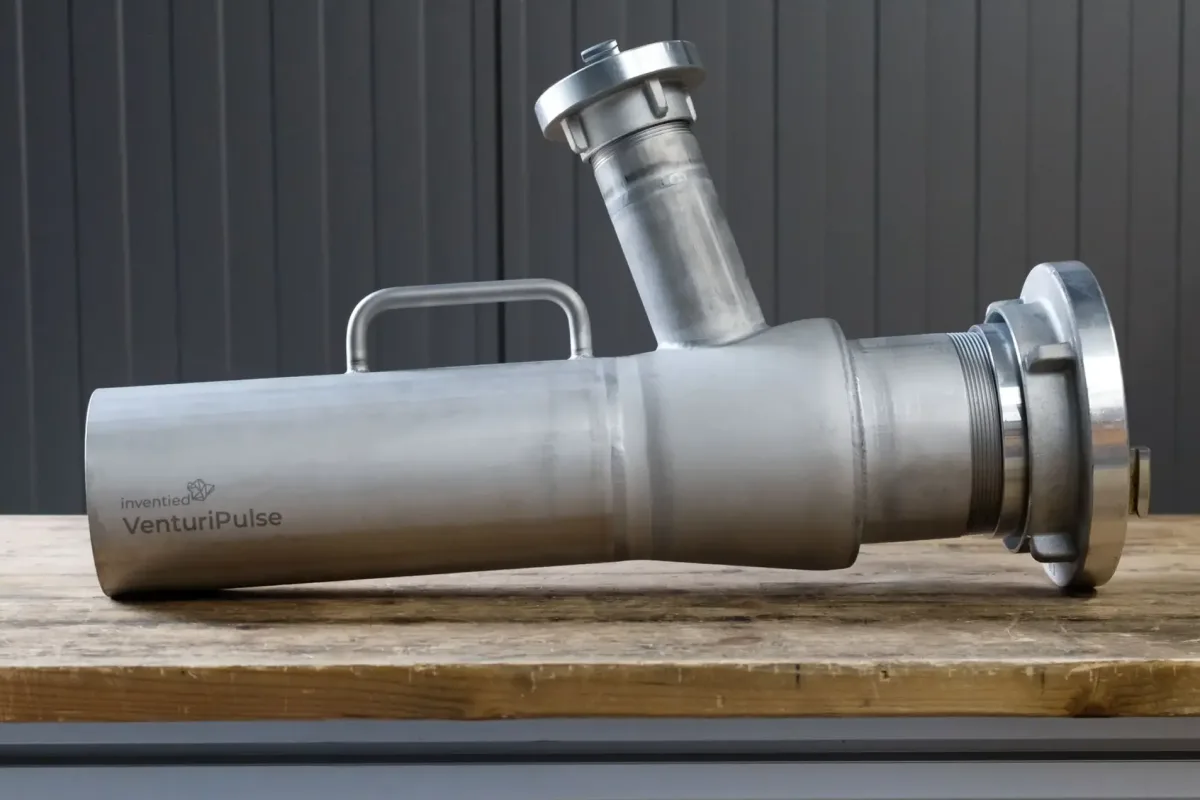

Fast and effective use
Help for eutrophic waters
The water aerator extends the functionality of submersible pumps by directing the pumped liquid sucked in by the pump through the constriction of the aerator. This creates a vacuum and ambient air is sucked in at the second inlet of the water aerator.
The ambient air sucked in mixes with the pumped medium, whereby an oxygen-enriched medium is returned to the water. In this way, eutrophic waters can be treated with sufficient air to prevent species extinction.
Technical data
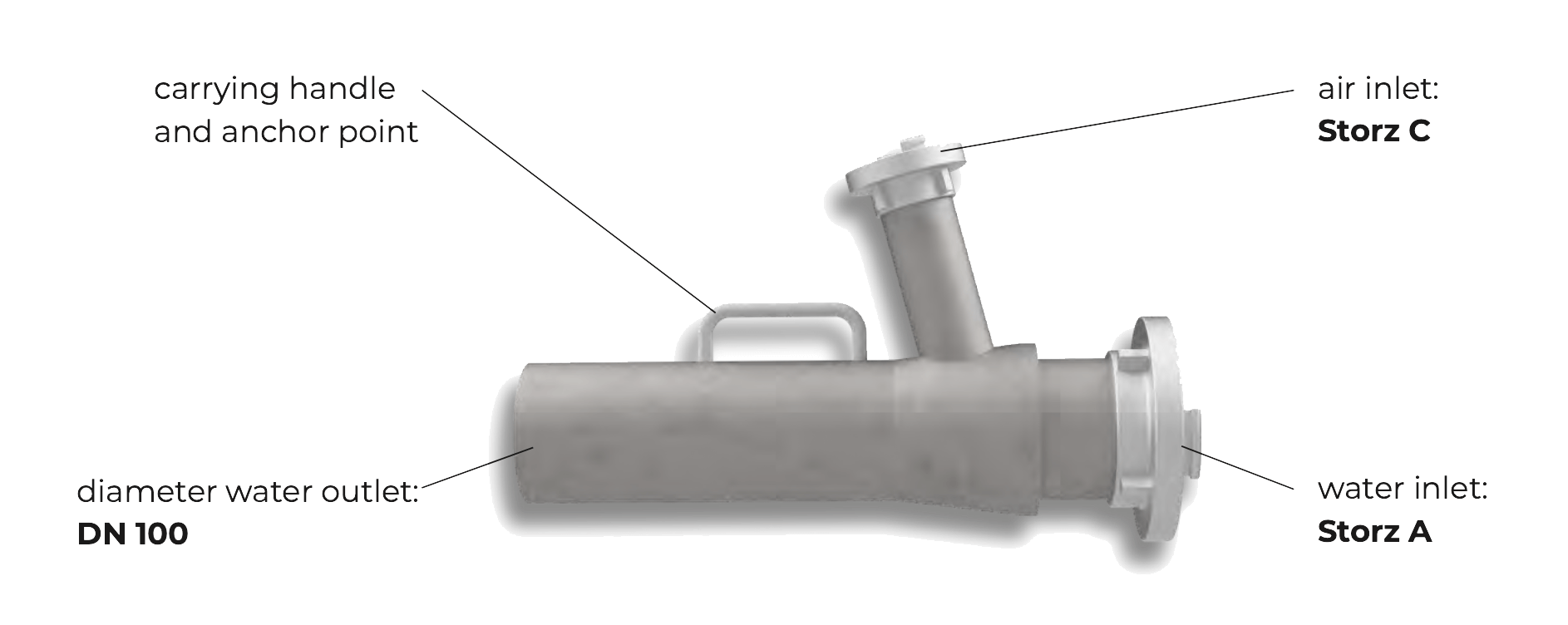
Dimensions
Dimensions (L x W x H)
Weight
Material
Maximum pressure
Recommended water depth
560 x 360 x 190 mm
7 kg
Stainless steel V2A
5 bar
0,5 – 2 m
Brochure (German)
Venturi-Pulse
Compatible with:
Wilo-Drain TP 100E
Chiemsee A & B
With the Wilo, up to 4000 l/min of ambient air can be supplied with a B suction hose and up to 2400 l/min with a C suction hose.
The following accessories are available:
- Suction hose with Storz C coupling on both sides
- Suction hose with Storz B coupling on both sides
- Reducer from Storz A to B
- Reducer from Storz B to C
Enquire now!
Simply fill out our contact form and let us know that you would like a non-binding quote for the VenturiPulse water aerator. Of course, you can also enquire about our other products at the same time.
Do you still have questions? We will give you the answers!
- Lakes that require remediation are often eutrophic or even hypertrophic, which indicates an excess of nutrients, especially phosphate. This leads to too much biomass forming in the upper layer of water, which consumes oxygen as it decomposes in the lower layer. This can result in the lake becoming oxygen-free at depth, which leads to the death of organisms that require oxygen. Toxic anaerobic decomposition products such as hydrogen sulphide and ammonia can form, and digested sludge develops on the lake bed. The phosphate it contains remains problematic, as it does not form an insoluble compound with trivalent iron and its fertilizing capacity is retained despite mixing, which is known as “tipping over” the lake. The enrichment of oxygen in bodies of water can prevent a body of water from tipping over.
- This is clearly explained in this video: Lake ecosystem – eutrophication
The ambient air is introduced directly into the water through the near-surface ventilation. This creates a fine bubble pattern that promotes oxygen enrichment in the water. These bubbles spread over a larger area and create slight waves that raise the surface of the water. This contributes to additional oxygen enrichment. As a result, survival zones for aquatic organisms are initially created in which sufficient oxygen is available. Over time, the oxygen content in the entire body of water increases and the overall water quality improves. Extensive experience in use has shown that this method of water aeration with a supply of up to 4000 l/min of ambient air is significantly more efficient than the suction of water, which is directed through hoses as spray water onto the water surface.
It is advisable to use at least two water aerators at the same location, which introduce ambient air in different directions in order to enrich zones with ambient air. Water aeration is particularly recommended at times of day when there is no sunlight, as photosynthesis then stops and less oxygen is enriched in the water. Ideally, it should be started before dusk. However, this should be done in close consultation with the relevant authorities or water boards.
The suction side of the pump used should never point towards the bottom so that bottom particles are not sucked in and distributed in the water. This prevents damage. This also ensures that no digested sludge is sucked in. The water aerator is only suitable for near-surface water aeration. The ideal operating depth is between 0.5 and 2 meters. With deep aeration, there is otherwise a risk of harmful substances such as hydrogen sulphide being washed out and stirred up. The water outlet of the water aerator should ideally be parallel to the floor – and should never be directed towards the floor. Otherwise there is a risk of the soil being washed out and sediments being stirred up.
The use of the water aerator creates a recoil on the outlet side of the aerator, which must be absorbed, otherwise the pump and water aerator may make uncontrolled movements. Depending on the ambient conditions, the recoil can be successfully absorbed by the following measures. The first option is to be preferred if possible:
- Use of ground pegs, lantern irons or equivalent functional parts to secure the pump to the ground or to restrict the movement of the pump
- Use in the paved bank area (stones)
- In certain cases, a lattice box or similar container may be suitable for lowering the pump with water aerator
- The water aerator alone has already been successfully tested with the following pumps:
- Wilo-Drain TP 100E
- Spechtenhauser Pumpen GmbH Model: Chiemsee A
- Spechtenhauser Pumpen GmbH Model: Chiemsee B; with reduction Storz A to B
- The VenturiPulse works with all pumps that have the same or better technical data than the Chiemsee B. Pumps with higher specifications than the Wilo-Drain TP 100E must not be used with VenturiPulse. Use is at your own risk. More information can be found in the operating instructions. However, we are always endeavoring to test and safely release further pump models. Please ask us about the models you require. If there is sufficient demand, we will be happy to test them!
As a rule of thumb, the greater the volume flow, the more ambient air is drawn in. In addition, the pump used must have at least one Storz B coupling. With the Wilo, up to 4000 l/min of ambient air can be supplied with a B suction hose and up to 2400 l/min with a C suction hose.
The water aerator is only suitable for near-surface water aeration. The ideal operating depth is between 0.5 and 2 meters. With deep aeration, there is otherwise a risk of harmful substances such as hydrogen sulphide being washed out and stirred up.
- PVC suction hose or equivalent or higher quality suction hose with Storz C coupling on both sides; optionally with strainer on a Storz C coupling to minimize contamination and injuries
- PVC suction hose or equivalent suction hose with Storz B coupling on both sides
- Reducer from Storz A to B
- Reducer from Storz B to C
We will be happy to advise you on which accessories you need for your specific application. You can often use materials that you already have in your office anyway.
It is strongly recommended that the responsible water authorities and/or water boards are involved in every operation and that the procedures are coordinated with each other! You should also find out about any other contacts that should be involved in your region.
Yes! The VenturiPulse has already been used successfully to prevent water from tipping over. You can find an example of a THW Pfaffenhofen operation here: Water aerated: Fish mortality prevented
- Was versteht man unter gekippten bzw. euthropierten Gewässern?
- Was versteht man unter gekippten bzw. euthropierten Gewässern?
- Seen, die saniert werden müssen, sind oft eutroph oder sogar hypertroph, was auf einen Überschuss an Nährstoffen, insbesondere Phosphat, hinweist. Dies führt dazu, dass sich in der oberen Wasserschicht zu viel Biomasse bildet, die bei ihrem Abbau in der unteren Schicht Sauerstoff verbraucht. Dies kann dazu führen, dass der See in der Tiefe sauerstofffrei wird, was zum Absterben von Sauerstoff benötigenden Organismen führt. Giftige anaerobe Abbauprodukte wie Schwefelwasserstoff und Ammoniak können sich bilden, und am Seeboden entsteht Faulschlamm. Das darin enthaltene Phosphat bleibt problematisch, da es keine unlösliche Verbindung mit dreiwertigem Eisen bildet und seine Düngekapazität trotz Durchmischung erhalten bleibt, was als “umkippen” des Sees bezeichnet wird. Durch die Anreicherung von Sauerstoff in Gewässern kann verhindert werden, das ein Gewässer kippt.
- Dieser Sachverhalt wird anschaulich in diesem Video erklärt: Ökosystem See – Eutrophierung
- Warum ist der VenturiPulse für die Belüftung von Gewässern geeignet und was unterscheidet den VenturiPulse von herkömmlichen Einsatztaktiken?
- Warum ist der VenturiPulse für die Belüftung von Gewässern geeignet und was unterscheidet den VenturiPulse von herkömmlichen Einsatztaktiken?
Durch die oberflächennahe Belüftung wird die Umgebungsluft direkt ins Wasser eingeführt. Dabei entsteht ein feines Blasenbild, das die Sauerstoffanreicherung im Wasser begünstigt. Diese Bläschen breiten sich in einem größeren Wirkungsbereich aus und erzeugen leichte Wellen, die die Oberfläche des Wassers erhöhen. Dies trägt zur zusätzlichen Sauerstoffanreicherung bei. Infolgedessen entstehen zunächst Überlebenszonen für aquatische Organismen, in denen ausreichend Sauerstoff vorhanden ist. Mit der Zeit steigt der Sauerstoffgehalt im gesamten Gewässer an, und die Wasserqualität verbessert sich insgesamt. Durch umfangreiche Erfahrungen im Einsatz hat sich gezeigt, dass diese Methode der Gewässerbelüftung mit einer Zufuhr von bis 4000 l/min Umgebungsluft deutlich effizienter ist als die Ansaugung von Wasser, das gezielt durch Schläuche als Spritzwasser auf die Wasseroberfläche geleitet wird.
- Wie viele VenturiPulse werden für den Einsatz benötigt?
- Wie viele VenturiPulse werden für den Einsatz benötigt?
Es empfiehlt sich, mindestens zwei Wasserbelüfter an derselben Stelle einzusetzen, die in verschiedene Richtungen Umgebungsluft einbringen, um Zonen mit Umgebungsluft anzureichern. Vor allem zu Tageszeiten ohne Sonnenlicht empfiehlt sich eine Gewässerbelüftung, da dann die Photosynthese ausetzt und weniger Sauerstoff im Gewässer angereichert wird. Es sollte idealerweise vor der Abenddämmerung angefangen werden. Dies sollte allerdings in enger Absprache mit den zuständigen Behörden oder Wasserverbänden.
- Wie wird bei der Verwendung des VenturiPulse sichergestellt, dass es zu keiner Schädigung des Gewässers kommt?
- Wie wird bei der Verwendung des VenturiPulse sichergestellt, dass es zu keiner Schädigung des Gewässers kommt?
Die Ansaugseite der verwendeten Pumpe sollte nie Richtung Boden zeigen, damit Bodenbestandteile nicht angesaugt werden und im Gewässer verteilt werden. So lassen sich Schäden vermeiden. So wird zudem sichergestellt, dass kein Faulschlamm angesaugt wird. Der Wasserbelüfter ist nur für die oberflächennahe Wasserbelüftung geeignet. Die ideale Einsatztiefe liegt zwischen 0,5 und 2 Meter. Bei einer Tiefenbelüftung besteht sonst die Gefahr, dass es zu Ausspülungen und Aufwirbelungen von schädlichen Stoffen wie Schwefelwasserstoffe kommt. Der Wasseraustritt des Wasserbelüfters sollte idealweise parallel zum Boden ausgeführt sein – und auf keinen Fall auf den Boden gerichtet sein. Sonst besteht die Gefahr, dass der Boden ausgeschwemmt wird und Sedimente aufgewirbelt werden.
- Wie werden Pumpen bei der Verwendung mit VenturiPulse im Wasser gesichert?
- Wie werden Pumpen bei der Verwendung mit VenturiPulse im Wasser gesichert?
Durch die Verwendung des Wasserbelüfters entsteht ein Rückstoß auf der Auslassseite des Belüfters, der unbedingt abgefangen werden muss, da sonst Pumpe und Wasserbelüfter unkontrollierte Bewegungen ausführen können. Durch folgende Maßnahmen kann der Rückstoß je nach Umgebungsbedingungen erfolgreich abgefangen werden. Die erste Möglichkeit ist, wenn möglich, zu bevorzugen:
- Verwendung von Erdnägeln, Laterneneisen oder gleichwertigen Funktionsteilen, um die Pumpe am Boden zu befestigen bzw. die Bewegung der Pumpe einzuschränken
- Die Verwendung im befestigten Uferbereich (Steine)
- In bestimmten Fällen kann sich eine Gitterbox oder ähnlicher Behälter zum Einlassen der Pumpe mit Wasserbelüfter eignen
- Mit welchen Pumpen ist der VenturiPulse kompatibel?
- Mit welchen Pumpen ist der VenturiPulse kompatibel?
Der Wasserbelüfter allein wurde bereits mit den folgenden Pumpen erfolgreich getestet:
- Wilo-Drain TP 100E
- Spechtenhauser Pumpen GmbH Modell: Chiemsee A
- Spechtenhauser Pumpen GmbH Modell: Chiemsee B; mit Reduzierung Storz A auf B
Bei allen Pumpen, die gleiche oder bessere technische Daten als die Chiemsee B aufweisen, funktioniert der VenturiPulse. Pumpen mit höheren Spezifikation als die Wilo-Drain TP 100E dürfen mit VenturiPulse nicht verwendet werden. Die Benutzung erfolgt auf eigenes Risiko. Mehr Informationen können der Betriebsanleitung entnommen werden. Wir sind aber stets bemüht weitere Pumpenmodelle zu testen und sicher freizugeben. Fragen Sie uns gerne wegen Wunschmodellen an. Bei ausreichender Nachfrage testen wir diese gerne!
- Welchen Einfluss hat die Wahl der Pumpe auf die Fördermenge an Umgebungsluft?
- Welchen Einfluss hat die Wahl der Pumpe auf die Fördermenge an Umgebungsluft?
Als Faustregel gilt: Umso größer der Volumenstrom ist, desto mehr Umgebungsluft wird angesaugt. Zudem muss die verwendete Pumpe mindestens über eine Storz-B-Kupplung verfügen. Mit der Wilo können mit einem B-Saugschlauch bis zu 4000 l/min und mit einem C-Saugschlauch bis zu 2400 l/min Umgebungsluft zugeführt werden.
- In welcher Tiefe kann der VenturiPulse eingesetzt werden?
- In welcher Tiefe kann der VenturiPulse eingesetzt werden?
Der Wasserbelüfter ist nur für die oberflächennahe Wasserbelüftung geeignet. Die ideale Einsatztiefe liegt zwischen 0,5 und 2 Meter. Bei einer Tiefenbelüftung besteht sonst die Gefahr, dass es zu Ausspülungen und Aufwirbelungen von schädlichen Stoffen wie Schwefelwasserstoffe kommt.
- Welches Zubehör wird für den VenturiPulse benötigt?
- Welches Zubehör wird für den VenturiPulse benötigt?
- PVC-Saugschlauch oder gleichwertiger bzw. höherwertiger Saugschlauch mit beidseitiger Storz C Kupplung; optional mit Sieb an einer Storz C Kupplung, um Verschmutzungen und Verletzungen zu minimieren
- PVC-Saugschlauch oder gleichwertiger Saugschlauch mit beidseitiger Storz B Kupplung
- Reduzierstück von Storz A auf B
- Reduzierstück von Storz B auf C
Gerne beraten wir Sie dazu, welches Zubehör Sie genau für Ihren Anwendungsfall benötigen. Oft können Sie auch Materialien benutzen, die sie sowieso schon in Ihrer Dienststelle haben.
- Wer muss bei der Gewässerbelüftung mit einbezogen werden?
- Wer muss bei der Gewässerbelüftung mit einbezogen werden?
Es wird dringend empfohlen, die zuständigen Wasserbehörden und oder Wasserverbände bei jedem Einsatz mit einzubeziehen und die Vorgehensweisen miteinander abzustimmen! Informieren Sie sich zudem über weitere Ansprechpartner, die ggf. in Ihrer Region miteinbezogen werden sollen.
- Gibt es Beispiele aus der Praxis?
- Gibt es Beispiele aus der Praxis?
Ja! DerVenturiPulse konnte bereits erfolgreich eingesetzt werden und das kippen von Gewässern verhindern. Einen beispielhaften Einsatz vom THW Pfaffenhofen finden Sie hier: Gewässer belüftet: Fischsterben verhindert
Teilen Sie uns auf Social Media

